HUMAN MACHINE INTERFACE
HMI stands for Human-Machine Interface, which refers to the interaction between a human and a machine, system, or device. It is a critical component in various fields, particularly in industrial, automotive, and technology sectors. An HMI allows users to control and monitor systems, usually by providing visual displays, touchscreens, or physical buttons.
Key Aspects of HMI:
- User Interface (UI): visual and interactive part where users can view system status, adjust settings, or control the system.
- Control Mechanism: This can include buttons, touchpads, dials, or even voice commands that allow users to control the machine.
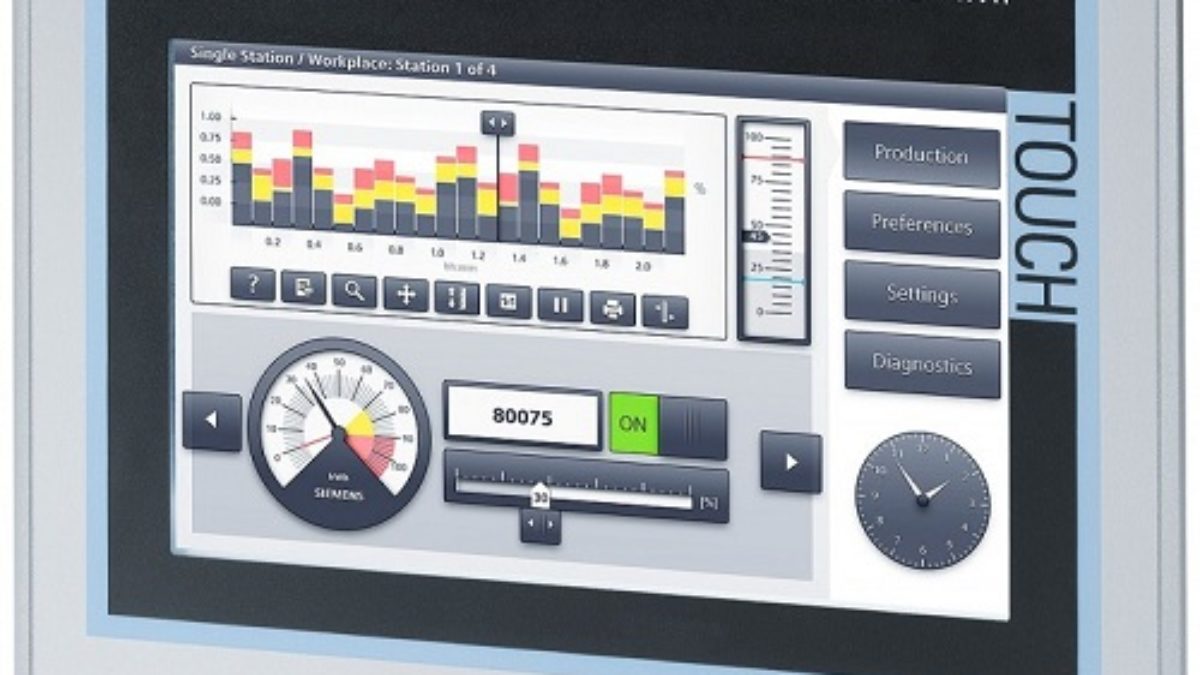
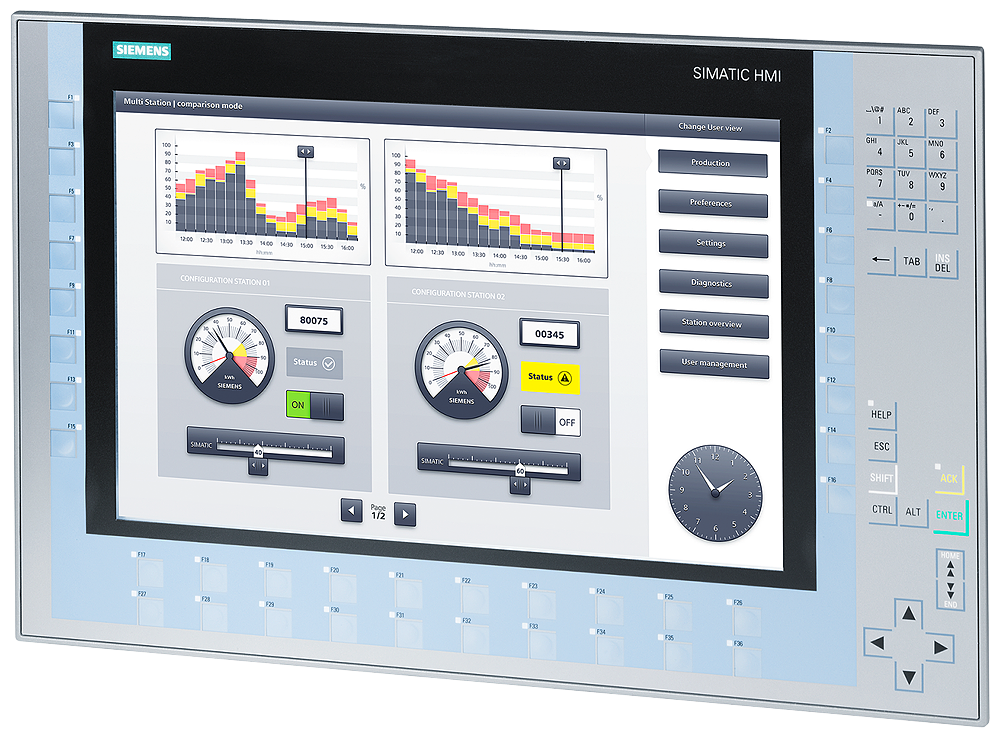
- Data Visualization: HMIs often present data in graphical formats, such as charts, gauges, or numerical readings, to help users make decisions or monitor processes.
- Feedback: Provides real-time feedback to users about the system’s operation, often in the form of alarms, warnings, or status indicators
Applications of HMI:
- Industrial Automation: In manufacturing or processing plants, HMIs are used to control machines, monitor production lines, and display data from sensors
- Automotive: In modern vehicles, the HMI controls infotainment systems, navigation, climate control, and even driver assistance features.
- Consumer Electronics: HMIs in devices like smartphones, smartwatches, and appliances enable interaction with the device and system control.
Types of HMIs:
- Basic HMI: Often just a simple interface with buttons or a small display
- Advanced HMI: Incorporates touchscreens, complex graphics, and multimedia features
- Embedded HMI: A more compact, integrated system, often found in devices like microwaves, washing machines, or vending machines.